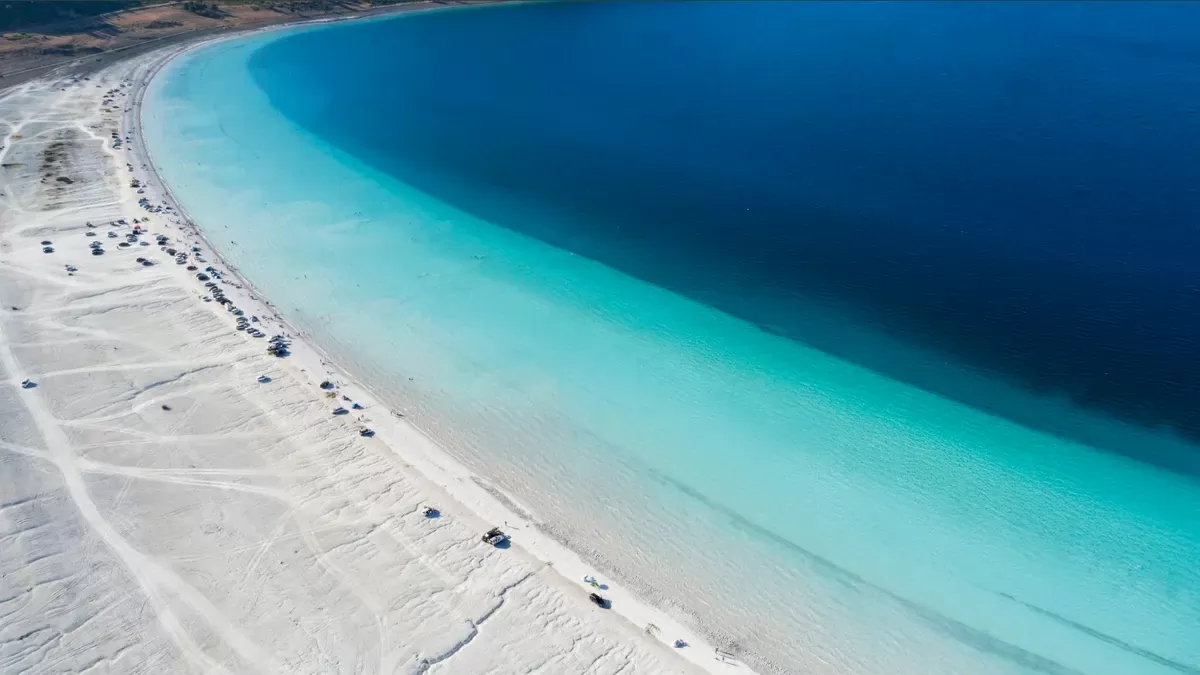
Lake Salda is known as the “Maldives of Türkiye”. (Source: Getty Images) |
Lake Salda, one of the deepest lakes in Türkiye, is located in the southwest of the country, 150 km from Antalya and 110 km from Denizli. The lake covers an area of nearly 4,400 hectares, with a depth of up to 196 m.
Known as the “Maldives of Turkey,” Lake Salda impresses with its white sand and crystal clear turquoise waters. According to CNN , the area around the lake is home to more than 300 species of plants and 30 species of birds. Thanks to its remote location, the landscape here remains untouched, attracting nature lovers and hiking enthusiasts.
Not only captivating tourists with its beautiful landscape, Lake Salda also excites scientists by offering an experience similar to standing on the ancient Jezero crater on Mars.
Professor Briony Horgan, an expert at the Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences at Purdue University (USA), said that in 2019, when he went to Türkiye with a NASA team to study Lake Salda, he was impressed by the landscape here, which was identical to outer space.
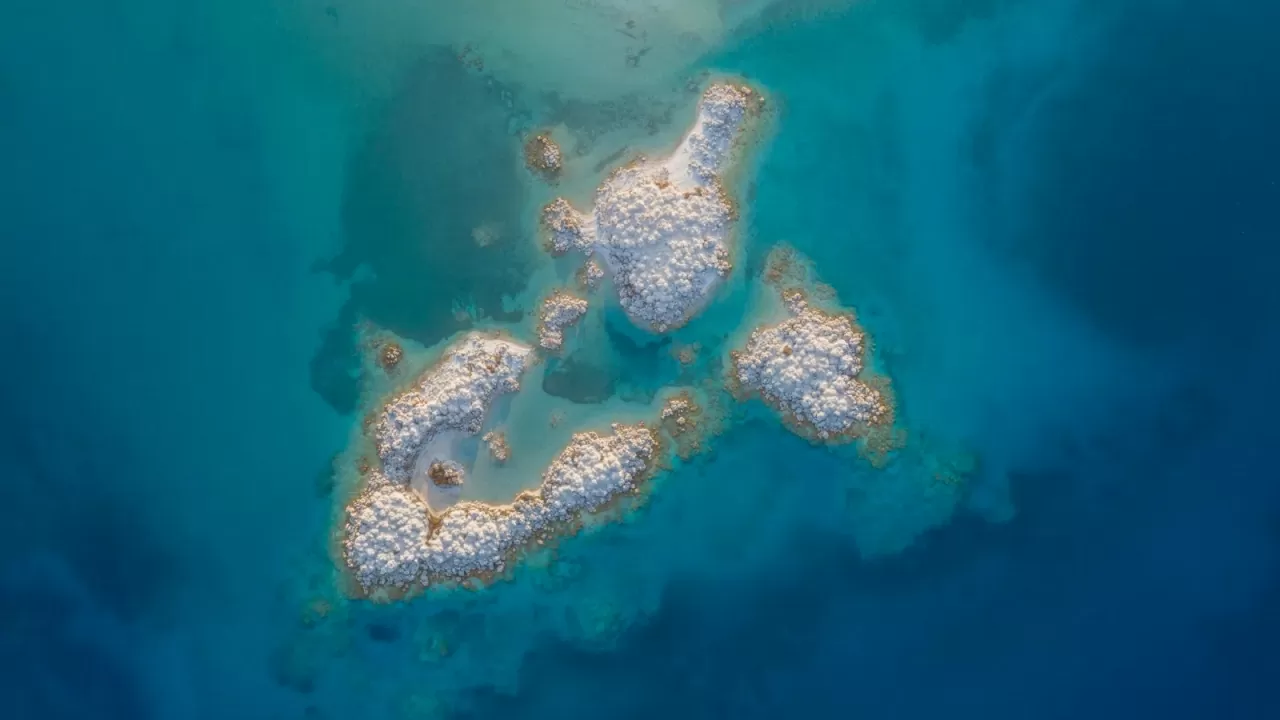
According to Live Science , this lake is the only place on Earth with geology and mineralogy comparable to ancient geological impact structures on the red planet. Accordingly, around the lake, scientists found layers of powdery Hydromagnesite, a carbonate mineral rich in magnesium, containing clues about ancient bacterial life.
Carbonates are important because they have the ability to preserve anything that exists in the environment, especially bacteria, organic matter and some components that provide evidence of past life, said Brad Garczynski, a planetary geologist at Western Washington University (USA).
Hydromagnesite deposits accumulate like coral reefs in Lake Salda. (Source: Getty Images) |
In addition to hydromagnesite, Lake Salda and Jezero Crater have another feature in common: delta landforms. These are layers of sediment that typically accumulate at the mouths of rivers that flow into lakes and other bodies of water. These deposits provide clues as to how water filled Jezero Crater. Studying the sediments in Lake Salda helped scientists narrow their search by pinpointing specific locations within the Martian crater.
With such valuable research values, in 2024, the International Geoheritage Committee (IUGS) included Lake Salda in the list of the world's top 100 geological sites.
Source: https://baoquocte.vn/mot-ky-quan-o-tho-nhi-ky-an-chua-bi-mat-tren-sao-hoa-309910.html






![[Photo] Flag-raising ceremony to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the Liberation of the South and National Reunification Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/175646f225ff40b7ad24aa6c1517e378)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam presents the title "Hero of Labor" to the Party Committee, Government and People of Ho Chi Minh City](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/08a5b9005f644bf993ceafe46583c092)
![[Photo] Performance of the Air Force Squadron at the 50th Anniversary of the Liberation of the South and National Reunification Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/30/cb781ed625fc4774bb82982d31bead1e)





























































































Comment (0)