In early September, Dutch Minister of Foreign Trade and Development Reinette Klever announced a change to export controls, requiring semiconductor machinery maker ASML to apply for a license to sell its DUV 1970i and 1980i photolithography machines to customers in China.
Additionally, ASML is required to obtain service licenses, as well as provide spare parts and software updates, for embedded lithography machines previously sold to Chinese customers.
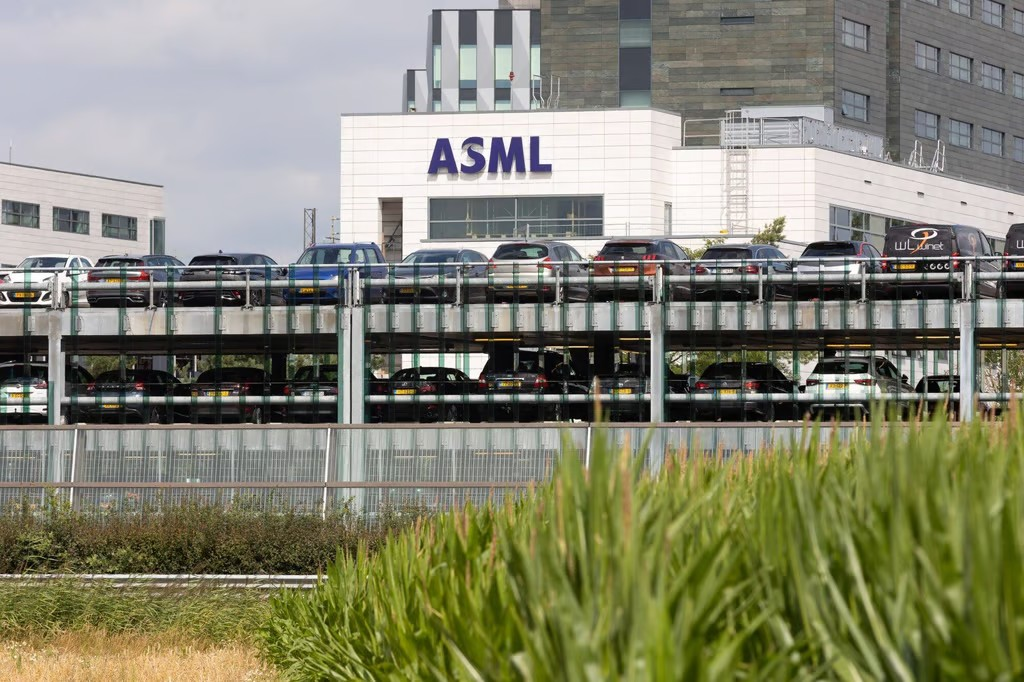

The move aims to align Dutch rules with tighter US trade restrictions – due to take effect in November 2023 – targeting China on national security grounds. Washington’s restrictions cover the 1970i and 1980i photolithography machines.
China's Ministry of Commerce affirmed that "China firmly opposes this".
The regulatory change is technical and does not affect this year's financial outlook, ASML said in a statement.
Maintenance services are crucial to maintaining productivity at semiconductor factories. Maintenance engineers need to be on call 24/7 in case of machine breakdowns. In China, the 1980i is a trusted piece of equipment for many chip factories because of its versatility, according to semiconductor experts.
The short-term impact of losing access to maintenance services on the chip industry is significant, according to a source close to ASML. Shen Bo, head of ASML China, said in an interview with China Daily in September 2023 that since entering the market in 1988, ASML has installed more than 1,000 machines there, including lithography tools and inspection solutions. ASML did not disclose how many machines were subject to the Dutch export restrictions.
Maintenance, however, is a smaller issue than the lack of new advanced lithography machines. Maintenance and finding spare parts is relatively easier than building lithography systems from scratch, sources close to ASML said.
Since 2019, mainland China, ASML's second-largest market by 2023 revenue, has been subject to increased export controls on lithography systems.
The Netherlands banned ASML from selling its most advanced EUV lithography machines – used for manufacturing chips below 7nm – and embedded DUV lithography machines, including the 2100i, 2050i, 2000i, 1970i and 1980i to China without a license.
Existing licenses for blacklisted Chinese companies will not be renewed and future applications will be rejected, according to Paul Van Gerven, editor of Dutch technology magazine Bits & Chips. Dry UV printers — older-generation machines that use air instead of water to improve resolution when printing complex circuit boards onto silicon wafers — are not currently subject to the restrictions, Van Gerven added.
ASML’s shipments to mainland China totaled €2.35 billion in the second quarter, or nearly half of its global sales. Its 2023 annual report showed that the company could only fulfill 50% of its orders from China due to a backlog.
(According to SCMP, Silicon)
Source: https://vietnamnet.vn/ban-dan-trung-quoc-anh-huong-nang-ne-tu-lenh-cam-moi-cua-ha-lan-2322620.html


![[Photo] Bustling construction at key national traffic construction sites](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/2/a99d56a8d6774aeab19bfccd372dc3e9)




![[Photo] Thousands of Buddhists wait to worship Buddha's relics in Binh Chanh district](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/3/e25a3fc76a6b41a5ac5ddb93627f4a7a)


























![[Photo] "Lovely" moments on the 30/4 holiday](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/1/26d5d698f36b498287397db9e2f9d16c)































































Comment (0)