 |
| Europe's number one economy is facing recession again. (Source: AP) |
Destatis data shows that in 2023, Germany's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) decreased by 0.3% compared to 2022. Thus, after the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic outbreak (2020), this is the second decline of the German economy this decade.
High inflation, rising interest rates and a weak global economy are the main reasons for the German economic slowdown.
High inflation reduces the purchasing power of private households, thus stifling consumption - an important pillar of Europe's "locomotive" economy.
To combat high inflation, the European Central Bank (ECB) has repeatedly raised interest rates, bringing them to historic highs. This has had a major impact on economic sectors, especially the construction industry. Germans' demand for homes has plummeted due to high financing costs.
Meanwhile, German exporters have been hit hard by the weak global economy. Global demand for goods has fallen, putting huge pressure on the country's manufacturers.
Germany’s top trading partners, especially China, have also struggled, with imports from Europe’s largest economy falling 3.0% and exports falling 1.8% last year.
In addition, persistent geopolitical uncertainties, from conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East to other tensions, have and continue to threaten supply chains, especially the vital Red Sea shipping lane.
Economist Laura Pagenhardt at the German Institute for Economic Research (DIW) said that many German companies are facing major difficulties and are delaying new investment plans. This can be seen clearly in the weak investment figures, especially in the new year 2024.
According to Destatis, 2023 is also a very difficult year for the federal budget. Higher interest costs, large energy subsidies and many other expenses have pushed the budget deficit into the "red alert" state.
According to preliminary assessments, Germany's budget deficit has increased by 82.7 billion euros, corresponding to a deficit of 2.0% of GDP.
Source

































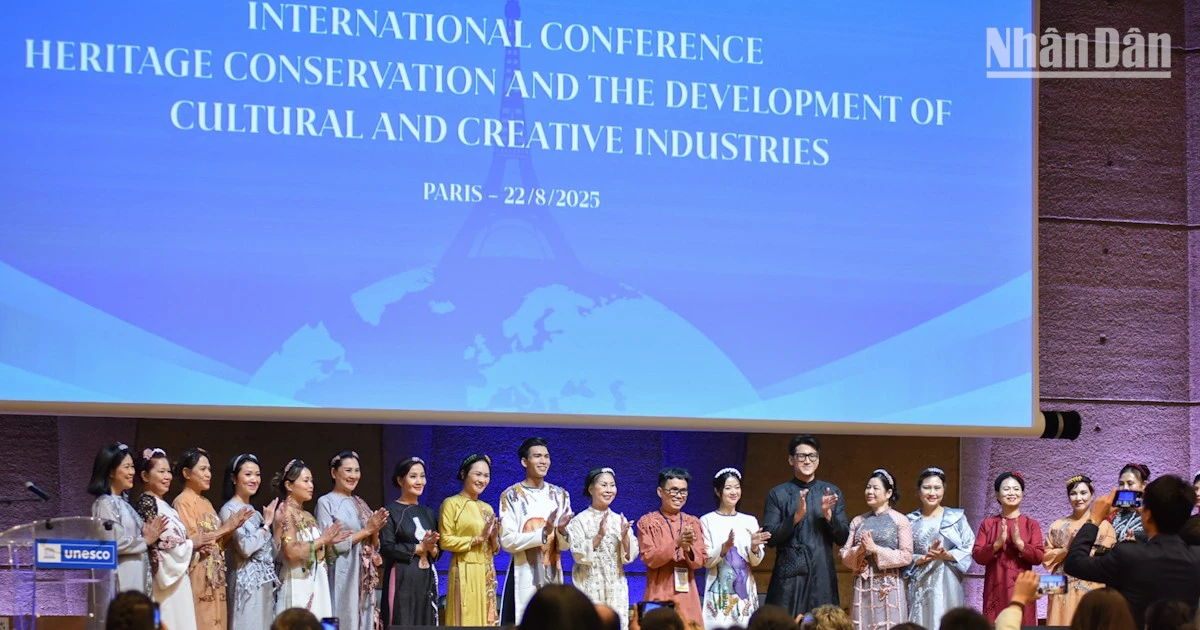
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends special political-artistic television show "Golden Opportunity"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/44ca13c28fa7476796f9aa3618ff74c4)






































































Comment (0)