China is gradually asserting its ambition to become self-sufficient in tropical fruit supply. After many years of research, this country of one billion people has successfully grown dragon fruit and recently durian - the "king of fruits" of Southeast Asia. The expansion of cultivated area shows the strategy of reducing dependence on imports while meeting the growing domestic demand.
From imported fruit to large-scale cultivation
Dragon fruit is not native to China but was introduced from Vietnam and some Southeast Asian countries, initially mainly imported for domestic consumption. Around 1990, when the Chinese people saw the great potential of this fruit, dragon fruit began to be experimentally grown in Guangxi and some other localities.
For the first 10 years, the dragon fruit industry in China was virtually stagnant. Before 2012, the total area planted with dragon fruit in the country was less than 50,000 acres (about 3,300 hectares). Pollination of the flowers at night was still done by hand.
The turning point of the Chinese dragon fruit industry began in 2012. Single-row and double-row planting models were tested, increasing the density from 400-500 trees to 800-2,200 trees/acre (equivalent to more than 666m2). In particular, supplementary night lighting technology opened up the possibility of year-round harvesting, increasing the number of fruit crops from 9-11 to 13-15.
In addition, thanks to great support from local authorities, especially since 2013, Guangxi has vigorously implemented the "High-quality Fruit Project", helping the local dragon fruit industry shift from small-scale planting to large-scale production.
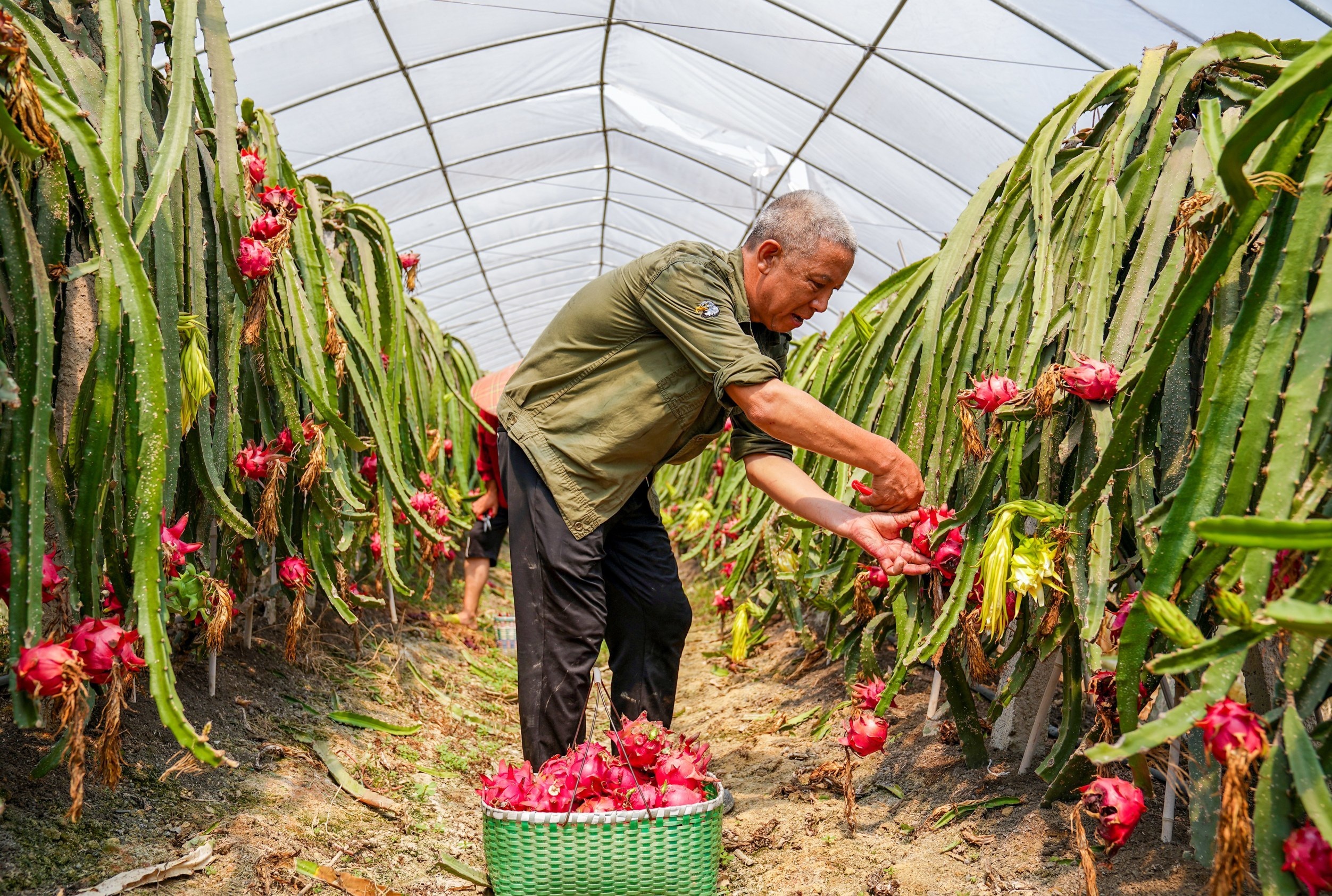

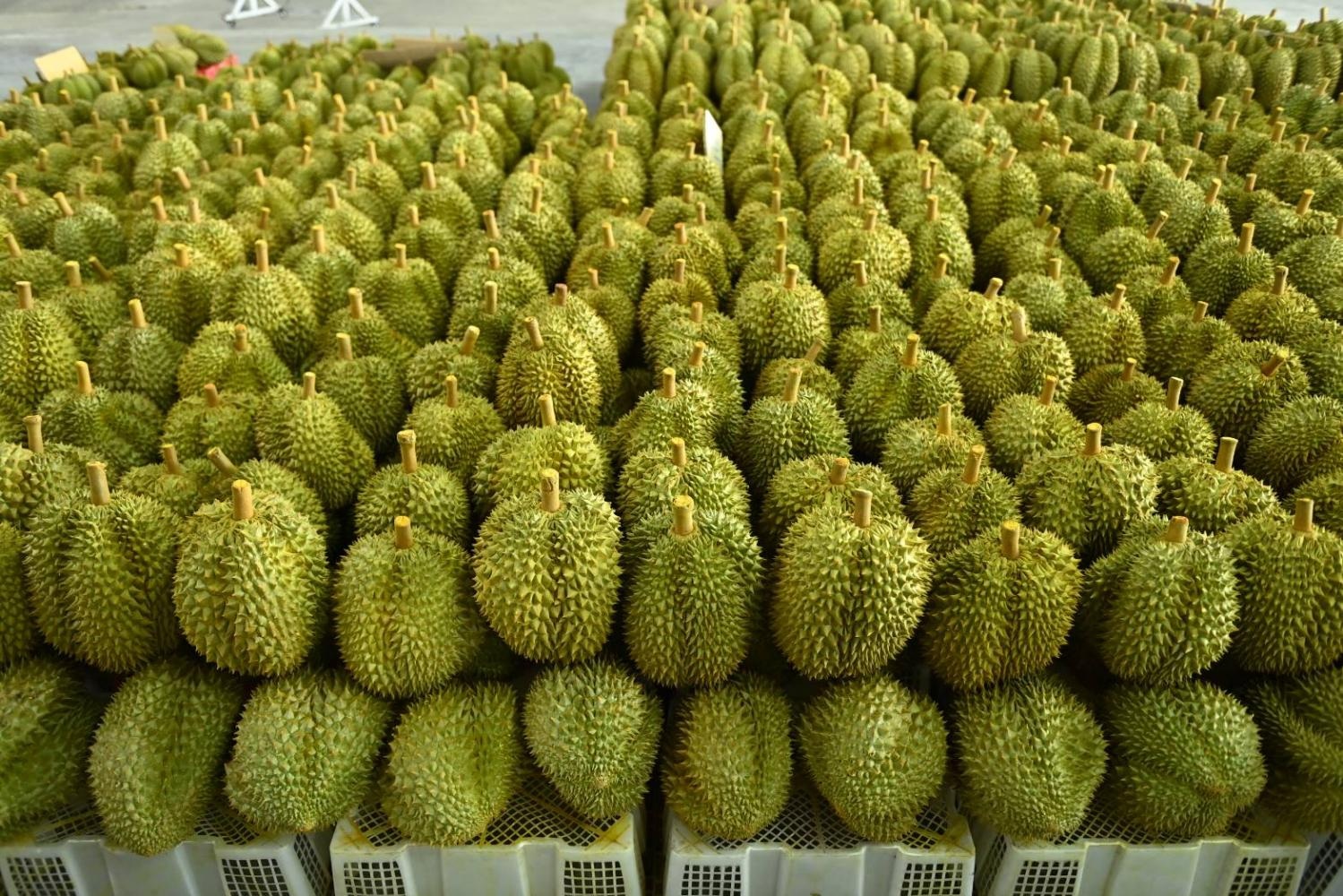
By 2021, China's dragon fruit growing area had exceeded 67,000 hectares, with an output of about 1.6 million tons, becoming the largest dragon fruit growing country in the world (Photo: Ifeng).
In less than 10 years, the area of dragon fruit cultivation in China has increased 15 times. By 2021, the area had exceeded 67,000 hectares, with an output of about 1.6 million tons. China has surpassed Vietnam to become the largest dragon fruit growing country in the world with a variety of dragon fruit varieties from white-fleshed, red-fleshed to yellow-fleshed.
The rapid growth of dragon fruit production in China is not only due to the continuous expansion of scale but also due to advances in cultivation technology, which have increased productivity. From 2016 to 2020, China's dragon fruit yield increased from 1.24 tons to 1.54 tons per mu, an increase of 23.82%.
In Nanning, dragon fruit growing areas apply many modern technologies. The models of growing dragon fruit in one row and two rows are improved from grape growing techniques; the LED night lighting system is researched by farmers themselves; the drip irrigation system integrates water - fertilizer and automatic spraying.
The production infrastructure is also synchronized, the cold storage and sorting workshop are located right in the garden. From production, supervision to preservation, digital technology is also applied. In particular, the smart management system continuously monitors temperature, soil humidity and environment, combined with 4-level cooling technology in the storage warehouse.

A dragon fruit garden in China at night, a system of lights hung high above shines down on each tree to stimulate flowering (Photo: Guangxi News Channel).
At present, Chinese dragon fruit is mainly distributed in Guangxi, Guangdong, Guizhou, Yunnan, Hainan and other regions. Guangxi and Guangdong are the two main growing areas, accounting for about 70% of the area.
Of which, Nanning (Guangxi) is the locality with an annual output of more than 430,000 tons, with an area of about 188,000 acres (equivalent to more than 12,500 hectares), as of 2023. Nanning accounts for about one-fifth of the total dragon fruit growing area in the country, becoming one of the largest dragon fruit producing regions in China.
Durian - a new link in the "made in China" fruit strategy
After the success of dragon fruit, durian is considered the next “big ambition” of the Chinese people. The world’s largest durian consumer market is stepping up testing of this fruit right in Hainan province, with the hope of self-sufficiency in supply.
Thanks to the tropical climate advantage in some southern provinces along with efforts in research and application of science and technology, China has initially successfully grown durian and harvested fruit after nearly 10 years, since 2018 when durian was put into large-scale cultivation. To increase the success rate, many businesses invited durian experts from Thailand and Malaysia to share their experiences.
Cultivation models were also adjusted to suit local soil conditions, with technical support from the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences and the Hainan Academy of Agricultural Sciences. As a result, the survival rate of crops reached 98%.
In 2023, about 1,400 acres (567ha) of durian in Sanya City (Hainan Province) will begin harvesting, yielding about 50 tons - marking the first large-scale harvest of domestic durian in China.
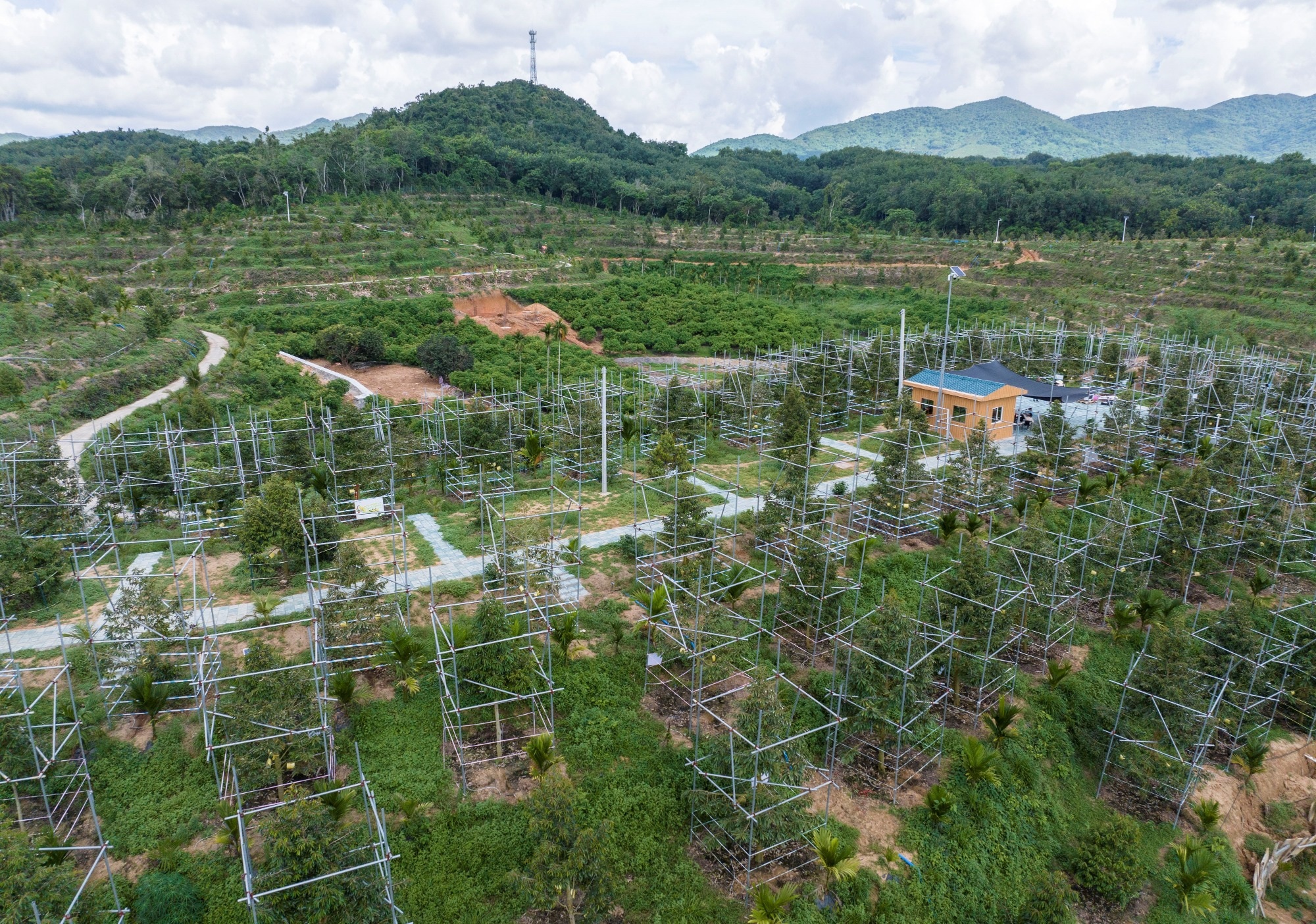

Durian plantation in Sanya, Hainan, with iron scaffolding installed around durian trees to protect against storms and other natural disasters (Photo: Getty).
By 2024, the durian acreage in Hainan will have increased to about 4,000 acres (1,619 hectares), with an estimated output of 260 tons. This year, China's domestic durian output is expected to reach nearly 2,000 tons, with a planting area of nearly 20,000 hectares, according to Sohu.
Speaking to Xinhua, many agricultural enterprises said that with an average yield of 40-50 fruits per tree and a production value of 1.2-1.5 million yuan/ha, durian will soon become a new "hot spot" of the country's agricultural industry.
In recent years, Hainan province has paid special attention to developing this plant. Specifically, in 2020, the Hainan Department of Science and Technology included durian in the list of key industries supported for research, and by 2022, the provincial Department of Agriculture and Rural Development continued to rank durian as one of 17 industries prioritized for development... The durian growing area in Hainan is expected to reach about 100,000 mu (equivalent to more than 6,600 hectares) within the next 2-3 years.
In order to develop durian varieties suitable for Hainan's climate, the Fruit Research Institute of the Hainan Academy of Agricultural Sciences is actively collecting high-quality durian genetic resources at home and abroad.
To date, the unit has collected more than 60 durian varieties from Malaysia, Thailand, Vietnam and several other countries. "We are applying hybridization and radiation mutation techniques to select new varieties with good resistance and high quality," said the Deputy Director of the Fruit Research Institute.

Improvements and innovations in planting techniques have solved the problem of durian being “difficult to adapt to soil and climate” in China. (Photo: Visual China).
According to China News, the price of domestically grown durian this year has dropped to around 50 yuan/kg (over 180,000 VND/kg) for Monthong durian. However, Musang King and Black Thorn durian grown in Hainan remain high, priced at 85-200 yuan/kg (310,000-750,000 VND/kg).
Speaking to Xinhua, Du Baizhong, chairman of the Hainan Durian Association and general manager of Youqi Agricultural Company, explained that Hainan durians are harvested when they are ripe on the tree, so they have a rich sweetness, a distinct aroma, and softer, more supple flesh. According to him, the scarcity and superior quality have pushed up the price of domestic durians, making them equal to high-end imported durians.
However, China is facing many challenges in developing tropical fruit crops in the context of rapidly increasing consumer demand. First of all, the climate factor. In Hainan, the locality still faces many obstacles such as limited land resources and being easily affected by storms, making durian production during the rainy season unstable and production costs much higher than in Southeast Asia.
For example, according to Produce Report, last June, a typhoon caused severe damage to major durian growing areas in Hainan, including Sanya, Luodong, and Baoding. Many durians that were about to be harvested were blown down by the wind, and tree trunks were broken and uprooted; from several dozen to several hundred trees were severely damaged.
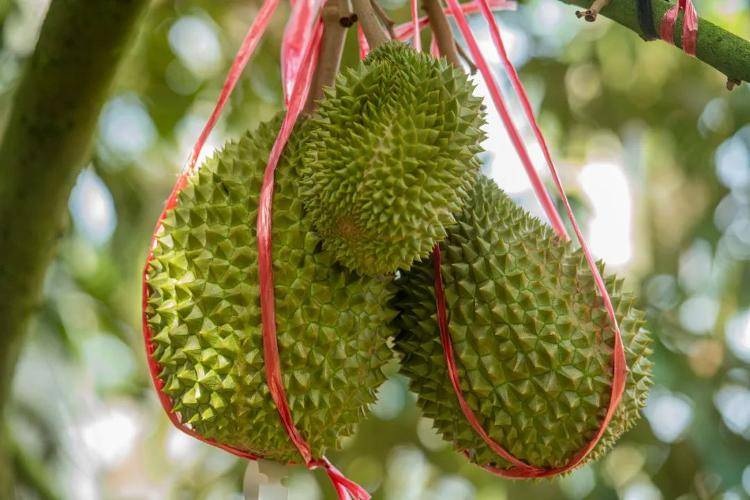

Some durian orchards in Hainan are facing problems such as poor pollination and low fruit set rates, due to factors such as seedling quality, cultivation management and climate conditions (Photo: Sohu).
In addition, Mr. Hoang Hai Kiet, Deputy Director of the Fruit Research Institute of the Hainan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, said that durian cultivation requires careful care, but some farmers lack skills, leading to unstable productivity. "In addition, the prevention of stem borers and leafhoppers, along with artificial pollination or flower and fruit preservation are still technological "bottlenecks" that need to be researched and overcome soon," he said.
Not only that, currently most of the planting area in China relies on imported varieties such as Monthong, Musang King or Black Thorn, while there are no domestic varieties.
According to Mr. Kiet, the Musang King variety has good adaptability, while the Black Thorn has high economic value, but both require careful care techniques. Meanwhile, the Monthong variety - which is famous for its easy fruit setting - has a problem with hard flesh and substandard sweetness when grown in Hainan, causing a decrease in quality.
How do Thailand, Vietnam and Malaysia cope?
China's "aggressive" expansion of durian growing areas not only shows its ambition to be self-sufficient in supply, but also puts great pressure on leading exporting countries such as Thailand and Vietnam.
Thailand is making efforts to promote a strategy of improving quality, labeling growing areas and tracing origins, while Vietnam is also focusing on increasing the area meeting export standards, controlling quality and expanding to new markets outside of China.
Specifically, after the incident of durian exported from Thailand to China being found to be contaminated with Basic Yellow 2 (BY2), the Thai Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives has established strict standards for durian exports, stipulating the minimum dry content of the segments for the Monthong (32%), Chanee (30%) and Kra Dum (28%) varieties to prevent the export of poor quality fruit, according to Thaitimes.

Thailand promotes quality improvement strategy, labeling growing areas and traceability (Photo: Bangkok Post).
In addition, all durian shipments from Thailand to China must be tested for pathogens (such as Salmonella, E. coli), heavy metals (cadmium) and banned substances such as BY2. In addition, Thailand is also promoting exports to China by rail to shorten the time, cut costs and ensure the quality of fresh fruit.
In Vietnam, authorities are stepping up the implementation of food safety control and traceability measures to cope with competition and challenges from China.
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment has also issued the Food Safety Control Process for Fresh Durian for Export (effective from August 4). Accordingly, the food safety control process for fresh durian for export covers everything from cultivation, harvesting, transportation to packaging and export, and requires registration, appraisal and safety certification for shipments.
Planting and packaging facilities must meet traceability standards, handle unsafe products and comply with certifications such as GAP, HACCP, ISO 22000... Exported products must meet pesticide residue limits and heavy metals according to Vietnamese standards and import market requirements, and must be labeled and listed by competent authorities.
Malaysia is also actively promoting durian exports, especially to the Chinese market, taking advantage of the growing demand and market opening. Previously, in June 2024, Malaysia successfully signed the Protocol on Phytosanitary Requirements for Fresh Durian Exports to China, opening up new market access opportunities for this Malaysian product.
To support durian growers in Pahang, the Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security of Malaysia has set up dedicated durian growing areas. In addition, the Long-Term Orchard Development Project has been implemented, through which 4,762 farmers have benefited, receiving support in production infrastructure, technical advice and agricultural equipment.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/kinh-doanh/tu-trong-thanh-long-den-sau-rieng-tham-vong-tu-chu-trai-cay-cua-trung-quoc-20250818005718684.htm





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the conference to review the 2024-2025 school year and deploy tasks for the 2025-2026 school year.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/2ca5ed79ce6a46a1ac7706a42cefafae)


![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives delegation of the Youth Committee of the Liberal Democratic Party of Japan](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/2632d7f5cf4f4a8e90ce5f5e1989194a)




















































































Comment (0)