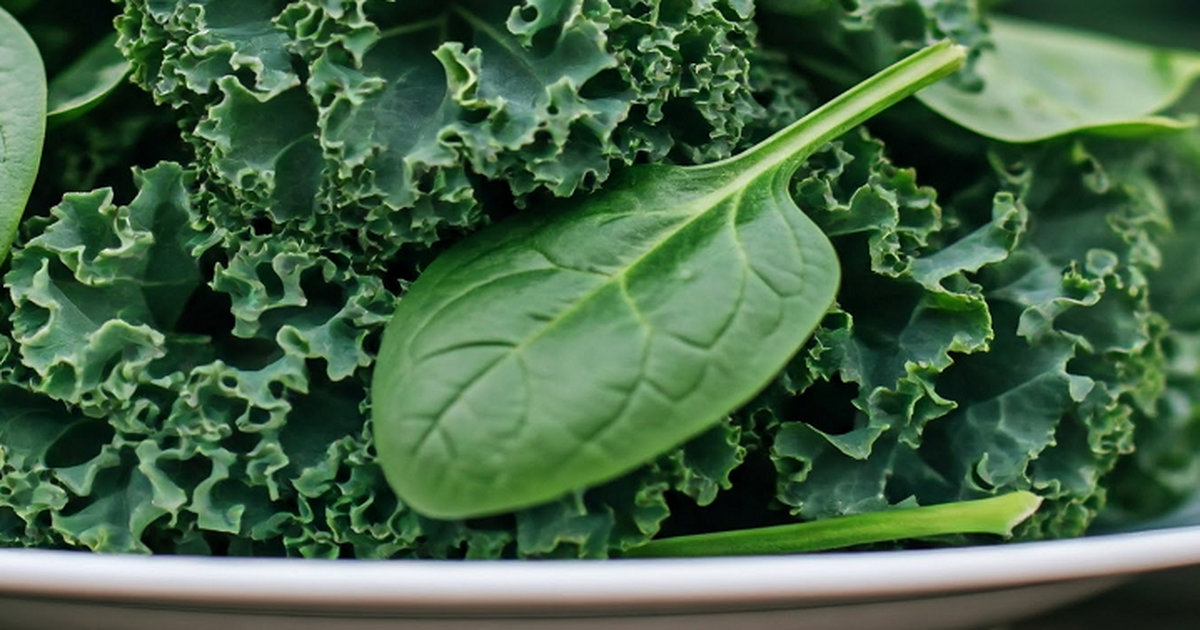
Kale is known as the "king of vegetables" because of its high nutritional content and many health benefits.
Nutritional composition of kale
The nutritional content of a cup of kale is about 67g, including:
- Vitamin A: 206% RDA (recommended daily allowance).
- Vitamin K: 684% RDA.
- Vitamin C: 134% RDA.
- Vitamin B6: 9% RDA.
- Manganese: 26% RDA.
- Calcium: 9% RDA.
- Copper: 10% RDA.
- Potassium: 9% RDA.
- Magnesium: 6% RDA.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine)
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Iron and phosphorus: 3% RDA.
- Fiber: 2g.
- Protein: 3g.
- Starch: 4g.
The fiber content in one cup of kale accounts for about 10% of your daily fiber intake, which helps keep you full longer and may help control diabetes.
The vitamin C content in kale is relatively high. 67g of kale provides about 134% of the daily vitamin C requirement, while 131g of citrus fruit only provides 113% of the requirement. Therefore, when you do not like to eat fruits such as oranges, tangerines, grapefruits, you can drink a glass of kale juice and still ensure the body's daily vitamin C needs.
In terms of vitamin A content (an important vitamin for immune function and healthy vision), 67 grams of kale provides about 206% of your daily vitamin A needs.
In addition, this vegetable also contains many important vitamins such as B1, B3, B6... and active ingredients with high antioxidant properties, thereby contributing to improving health, enhancing resistance and preventing the formation of malignant tumors.
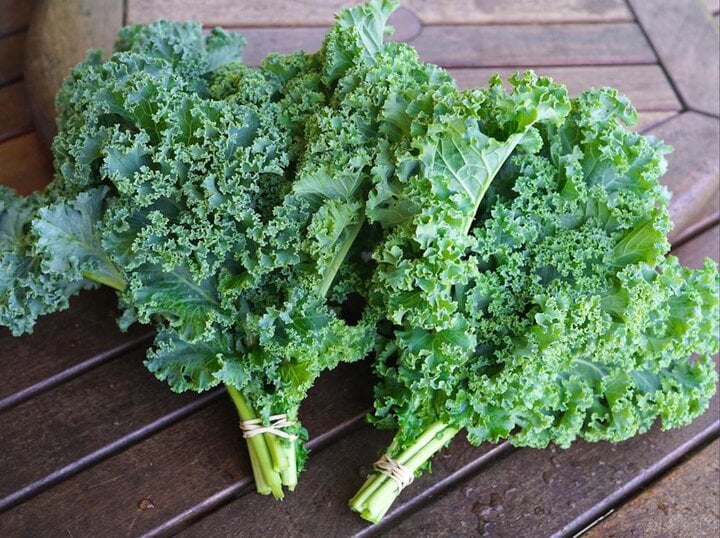

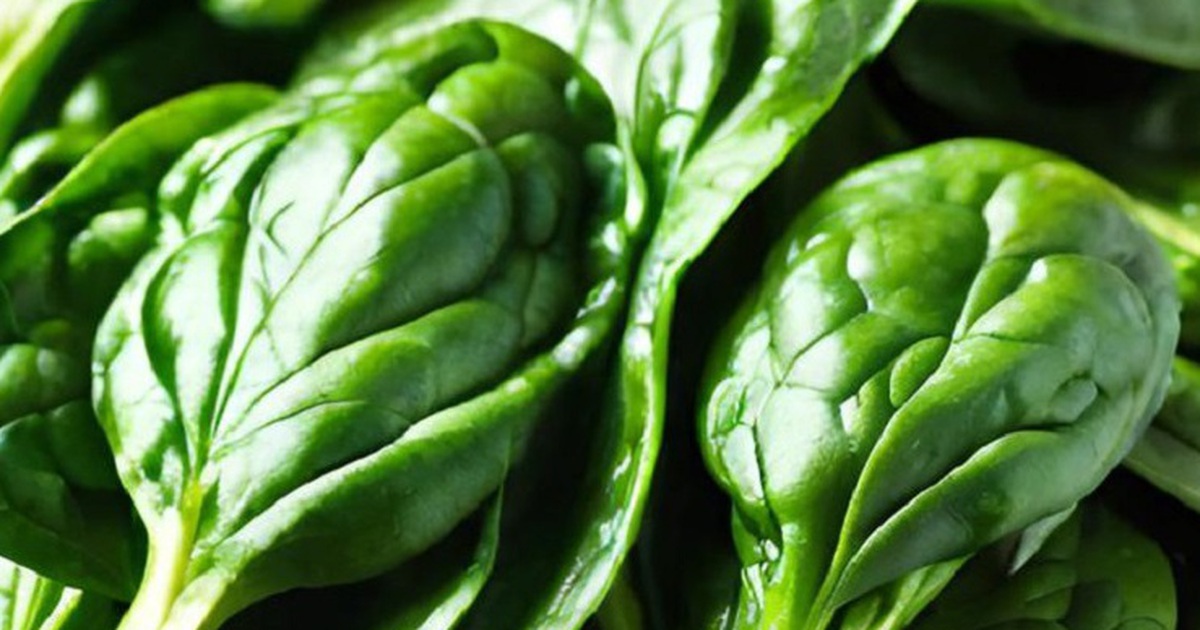
Kale is rich in calcium.
Kale has twice the calcium content of eggs and milk.
Associate Professor, Dr. Nguyen Thi Lam - former Deputy Director of the National Institute of Nutrition said that calcium is a mineral that helps the body form strong bones and teeth, ensuring normal nerve function and blood clotting.
100g of kale has about 250mg of calcium, while the same index in milk is 110mg, eggs are 50mg. Kale is a good source of calcium for the body.
Some studies have shown that kale contains compounds with anti-cancer properties, specifically glucosinates. Glucosinates work by inhibiting and slowing tumor growth as well as enzymes related to cancer.
In particular, kale is good for pregnant mothers and children. A cup of kale has only 36 calories but has up to 3 grams of fiber, meeting 10% of the calcium needs of pregnant mothers. At the same time, it provides vitamin C, vitamin A and B vitamins to help strengthen the immune system, ensuring stable growth of the fetus.
Kale is notable for its high vitamin K content, which supports the circulatory system for pregnant women, ensuring an abundant supply of blood to nourish the fetus through the placenta. For young children, kale is a rich source of calcium for bone development.
According to the nutritionist, kale can be made into many delicious and attractive dishes. However, if the vegetable source is guaranteed, eating it raw, mixing it in salads or making smoothies will help the body receive the most nutrients.
However, people with blood problems such as blood thinners, people taking cardiovascular support medications should consult a doctor before eating.
When preparing, avoid cooking at high temperatures because it is easy to lose nutrients. In particular, do not use too much kale because it is rich in nutrients. Instead, combine it with many other vegetables or foods to make the meal more diverse and balanced, which will bring more benefits to the body.
Source





![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 80th Anniversary of the Cultural Sector's Traditional Day](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/23/9f771126e94049ff97692935fa5533ec)































































































Comment (0)