Antibiotic resistance is responsible for around 5 million deaths a year globally. Experts predict that global antibiotic consumption could rise to 75.1 billion doses daily by 2030.
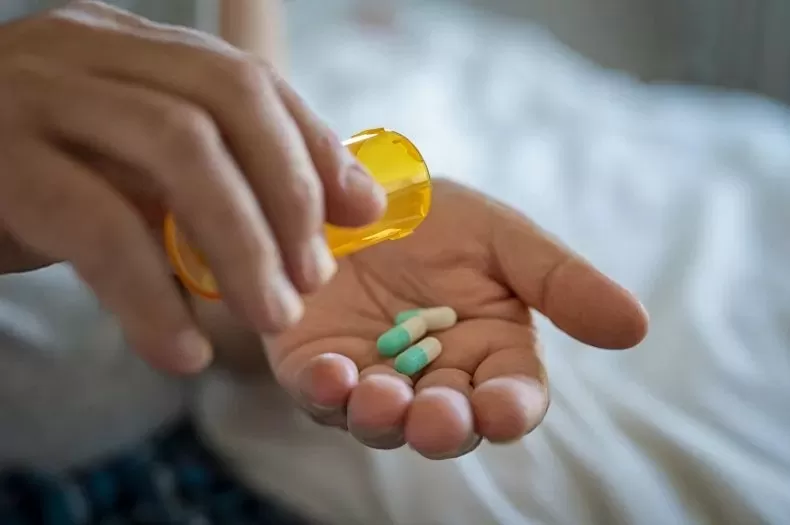 |
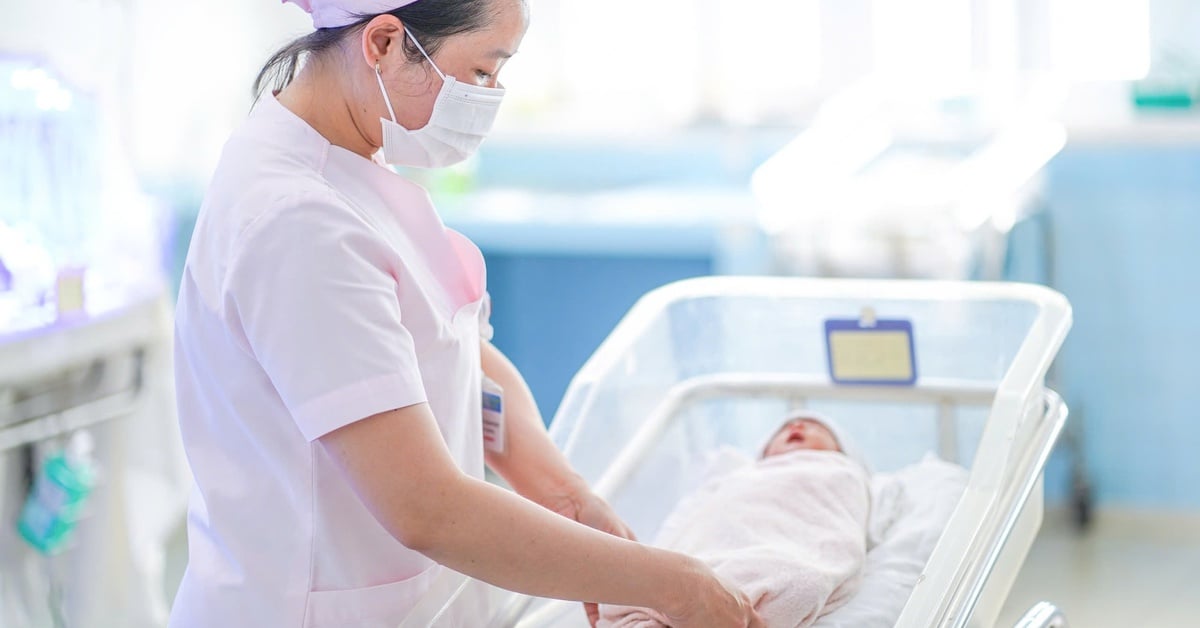
| Antibiotic resistance is causing about 5 million deaths a year globally. (Source: Getty Images) |
Global antibiotic use has increased by 21% since 2016, raising serious concerns about the risk of antibiotic resistance, according to a new study. Analysis of data from 67 countries shows this alarming upward trend.
The study, led by Dr. Eili Klein, senior researcher at the One Health Trust (OHT), found that antibiotic sales in the countries surveyed increased from 29.5 billion doses per day in 2016 to 34.3 billion doses in 2023, a 16.3% increase. Total global antibiotic use is now estimated to be 49.3 billion doses per day.
Notably, middle-income countries saw a 9.8% increase between 2016 and 2019, while high-income countries saw a 5.8% decrease. The 2020 Covid-19 pandemic has temporarily reduced antibiotic use, particularly in developed countries, where it decreased by 17.8%.
According to the Lancet , antibiotic resistance is causing about 5 million deaths each year globally. In the US alone, about 2.8 million people are infected with drug-resistant bacteria, of which 35,000 die.
Experts predict that global antibiotic consumption could rise to 75.1 billion doses per day by 2030, a 52.3% increase. Dr. Klein stressed that there is no simple solution to the problem and called for policy and cultural changes in the health sector.
Source



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the conference to review the 2024-2025 school year and deploy tasks for the 2025-2026 school year.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/2ca5ed79ce6a46a1ac7706a42cefafae)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives delegation of the Youth Committee of the Liberal Democratic Party of Japan](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/2632d7f5cf4f4a8e90ce5f5e1989194a)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends special political-artistic television show "Golden Opportunity"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/8/22/44ca13c28fa7476796f9aa3618ff74c4)






























































































Comment (0)